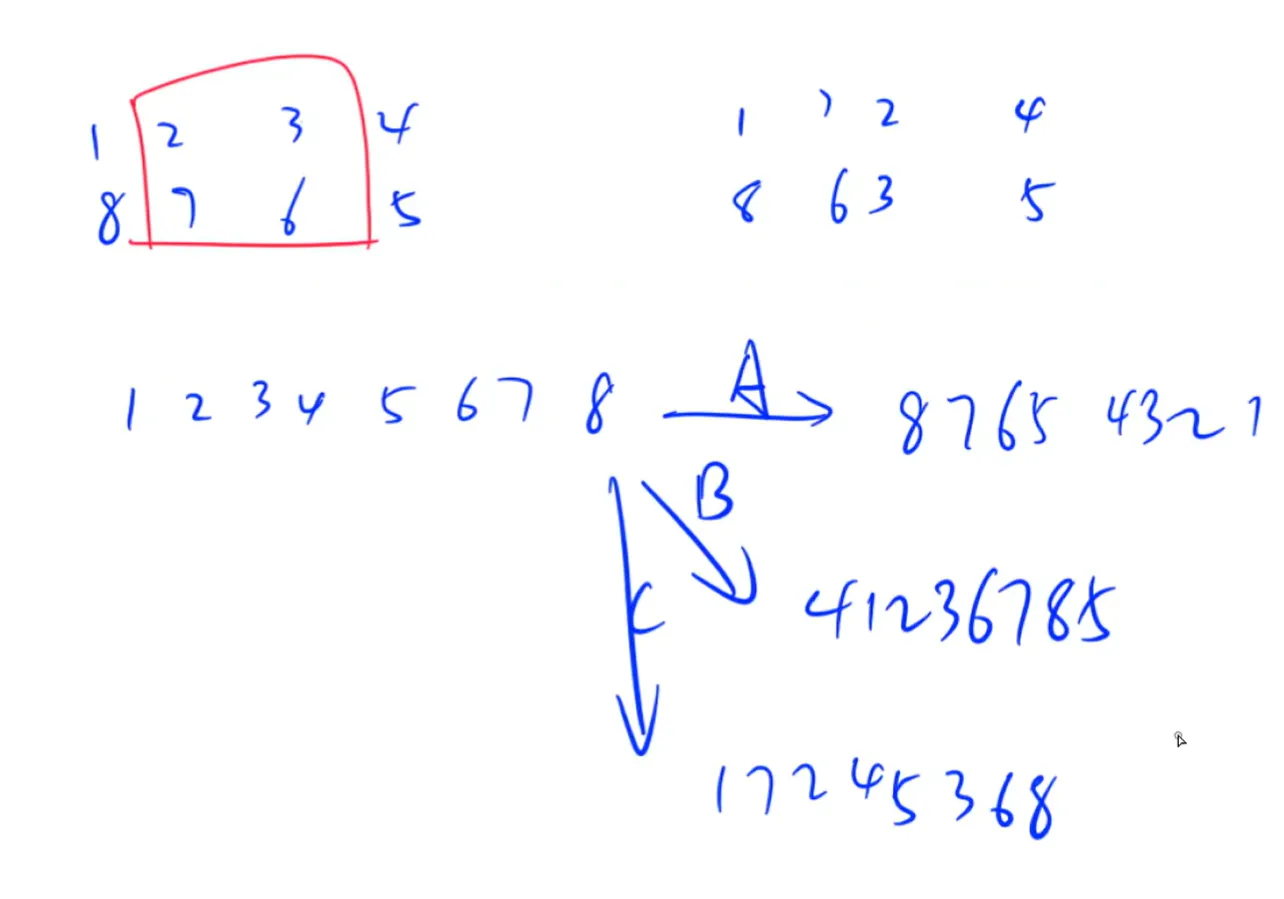广度优先搜索与深度优先搜索,这里不多赘述。
时间: 差不多,都高于O ( n + m ) O(n+m) O ( n + m )
空间: BFS 空间消耗远大于 DFS,对于一个满二叉树,每出队一个节点,就会入队两个节点,在第 k k k 2 k 2^k 2 k
总结:DFS 适合找任意可行解,BFS 适合找全局最优解。
宽搜:queue
一般解决遍历/连通性问题,DFS/BFS 都可以做。
深搜只能知道是否连通,但不保证最短距离。
而深搜的码量比较少。
AcWing1112
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 110 ;int n;char g[N][N];bool st[N][N];int xa, ya, xb, yb;bool Dfs (int x, int y) if (g[x][y] == '#' ) return false ; if (x == xb && y == yb) return true ; st[x][y] = true ; int dx[] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }, dy[] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) { int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i]; if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= n) continue ; if (st[a][b]) continue ; if (Dfs (a, b)) return true ; } return false ; } int main () int T; cin >> T; while (T--) { cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) cin >> g[i]; memset (st, 0 , sizeof (st)); cin >> xa >> ya >> xb >> yb; if (Dfs (xa, ya)) printf ("YES\n" ); else printf ("NO\n" ); } return 0 ; }
A1113
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 25 ;int n, m;char g[N][N];bool st[N][N];int DFS (int x, int y) int cnt = 1 ; st[x][y] = 1 ; int dx[] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }, dy[] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) { int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i]; if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m) continue ; if (g[a][b] != '.' ) continue ; if (st[a][b]) continue ; cnt += DFS (a, b); } return cnt; } int main () while (cin >> m >> n, n || m) { memset (st, 0 , sizeof (st)); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) cin >> g[i]; int x, y; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < m; ++j) { if (g[i][j] == '@' ) { x = i; y = j; } } } cout << DFS (x, y) << endl; } return 0 ; }
尽可能地减少分支。
AcWing1116
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 11 ;int n, m;int ans;bool st[N][N];int dx[] = {-2 , -1 , 1 , 2 , 2 , 1 , -1 , -2 };int dy[] = {1 , 2 , 2 , 1 , -1 , -2 , -2 , -1 };void DFS (int x, int y, int sum) if (sum == n * m) { ans++; return ; } if (st[x][y]) return ; st[x][y] = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i]; if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >=m) continue ; if (st[a][b]) continue ; DFS (a, b, sum + 1 ); } st[x][y] = false ; } int main () int T; cin >> T; while (T--) { int x, y; cin >> n >> m >> x >> y; ans = 0 ; DFS (x, y, 1 ); printf ("%d\n" , ans); } return 0 ; }
AcWing1117
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 21 ;int n;string word[N]; int g[N][N];int used[N];int ans;void DFS (string dragon, int last) ans = max ((int )dragon.size (), ans); used[last]++; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) if (g[last][i] && used[i] < 2 ) DFS (dragon + word[i].substr (g[last][i]), i); used[last]--; } int main () cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) cin >> word[i]; char start; cin >> start; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) for (int j = 0 ; j < n; ++j) { string a = word[i], b = word[j]; for (int k = 1 ; k < min (a.size (), b.size ()); ++k) if (a.substr (a.size () - k, k) == b.substr (0 , k)) { g[i][j] = k; break ; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) if (word[i][0 ] == start) DFS (word[i], i); cout << ans << endl; return 0 ; }
P1118
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 10 ;int n;int p[N];int group[N][N];bool st[N];int ans = N;int gcd (int a, int b) if (b == 0 ) return a; return gcd (b, a % b); } bool check (int group[], int gc, int i) for (int j = 0 ; j < gc; ++j) { if (gcd (p[group[j]], p[i]) > 1 ) return false ; } return true ; } void DFS (int g, int gc, int tc, int start) if (g >= ans) return ; if (tc == n) ans = g; bool flag = true ; for (int i = start; i < n; ++i) { if (!st[i] && check (group[g], gc, i)) { st[i] = true ; group[g][gc] = i; DFS (g, gc + 1 , tc + 1 , i + 1 ); st[i] = false ; flag = false ; } } if (flag) DFS (g + 1 , 0 , tc, 0 ); } int main () cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) cin >> p[i]; DFS (1 , 0 , 0 , 0 ); cout << ans << endl; return 0 ; }
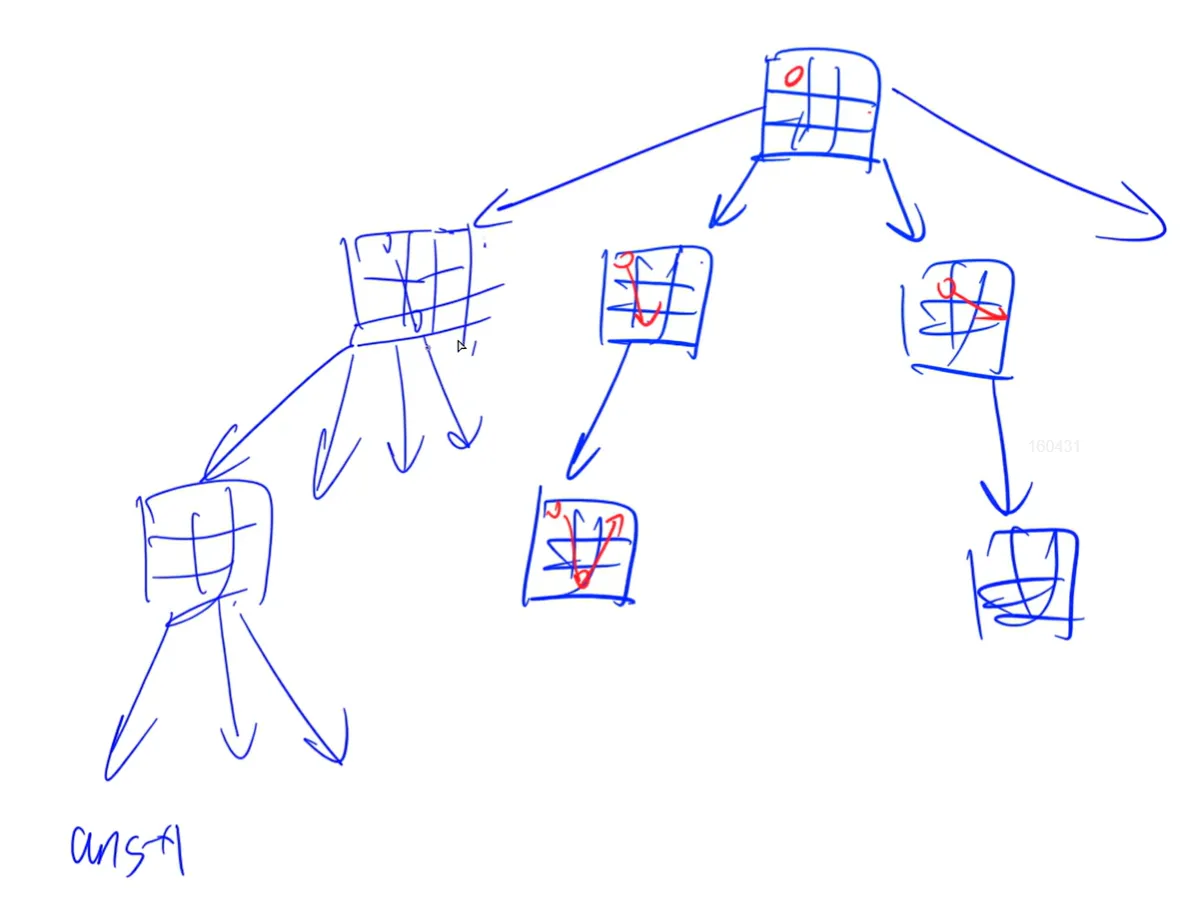
不管什么搜索,都可以对应出一个搜索树,如果中间可以判断这个子树一定不合法,那么就没必要接着往下搜了。
优化搜索顺序 大部分情况下,我们应该先搜索分支较少的节点。
排除等效冗余 不搜索重复的状态,不考虑顺序的话就采用组合的方法来搜索。
可行性剪枝 搜到一半发现不合法了。
最优性剪枝 当搜着发现一定不是最优解,那么就不继续搜了
记忆化搜索 其实就是 DP
AcWing165
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 20 ;int n, m;int w[N];int sum[N];int ans = N;void DFS (int u, int k) if (k >= ans) return ; if (u == n) { ans = k; return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < k; ++i) if (sum[i] + w[u] <= m) { sum[i] += w[u]; DFS (u + 1 , k); sum[i] -= w[u]; } sum[k] = w[u]; DFS (u + 1 , k + 1 ); sum[k] = 0 ; } int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) cin >> w[i]; sort (w, w + n); reverse (w, w + n); DFS (0 , 0 ); cout << ans << endl; return 0 ; }
AcWing166
AcWing166
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> using namespace std;#define lowbit(x) ((x) & (-x)) const int N = 9 , M = 1 << N;int ones[M], mp[M];int row[N], col[N], cell[3 ][3 ]; char str[100 ];void init () for (int i = 0 ; i < N; ++i) row[i] = col[i] = (1 << N) - 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++i) for (int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; ++j) cell[i][j] = (1 << N) - 1 ; } int get (int x, int y) return row[x] & col[y] & cell[x / 3 ][y / 3 ]; } void draw (int x, int y, int t, bool is_set) if (is_set) str[x * N + y] = '1' + t; else str[x * N + y] = '.' ; int v = 1 << t; if (!is_set) v = -v; row[x] -= v; col[y] -= v; cell[x / 3 ][y / 3 ] -= v; } bool DFS (int cnt) if (!cnt) return true ; int minv = 10 ; int x, y; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < N; j++) { if (str[i * N + j] == '.' ) { int state = get (i, j); if (ones[state] < minv) { minv = ones[state]; x = i, y = j; } } } } int state = get (x, y); for (int i = state; i; i -= lowbit (i)) { int t = mp[lowbit (i)]; draw (x, y, t, true ); if (DFS (cnt - 1 )) return true ; draw (x, y, t, false ); } return false ; } int main () for (int i = 0 ; i < N; ++i) mp[1 << i] = i; for (int i = 0 ; i < 1 << N; ++i) for (int j = 0 ; j < N; ++j) ones[i] += i >> j & 1 ; while (scanf ("%s" , str), str[0 ] != 'e' ) { init (); int cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 , k = 0 ; i < N; ++i) for (int j = 0 ; j < N; ++j, ++k) { if (str[k] != '.' ) { int t = str[k] - '1' ; draw (i, j, t, true ); } else cnt++; } DFS (cnt); puts (str); } return 0 ; }
AcWing167
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 70 ;int n;int w[N], sum, length;bool st[N];bool DFS (int u, int s, int start) if (u * length == sum) return true ; if (s == length) return DFS (u + 1 , 0 , 0 ); for (int i = start; i < n; ++i) { if (st[i]) continue ; if (s + w[i] > length) continue ; st[i] = true ; if (DFS (u, s + w[i], i + 1 )) return true ; st[i] = false ; if (!s) return false ; if (s + w[i] == length) return false ; int j = i; while (j < n && w[j] == w[i]) j++; i = j - 1 ; } return false ; } int main () while (cin >> n, n) { memset (st, 0 , sizeof (st)); sum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { cin >> w[i]; sum += w[i]; } sort (w, w + n); reverse (w, w + n); length = 1 ; while (true ) { if (sum % length == 0 && DFS (0 , 0 , 0 )) { cout << length << endl; break ; } length++; } } return 0 ; }
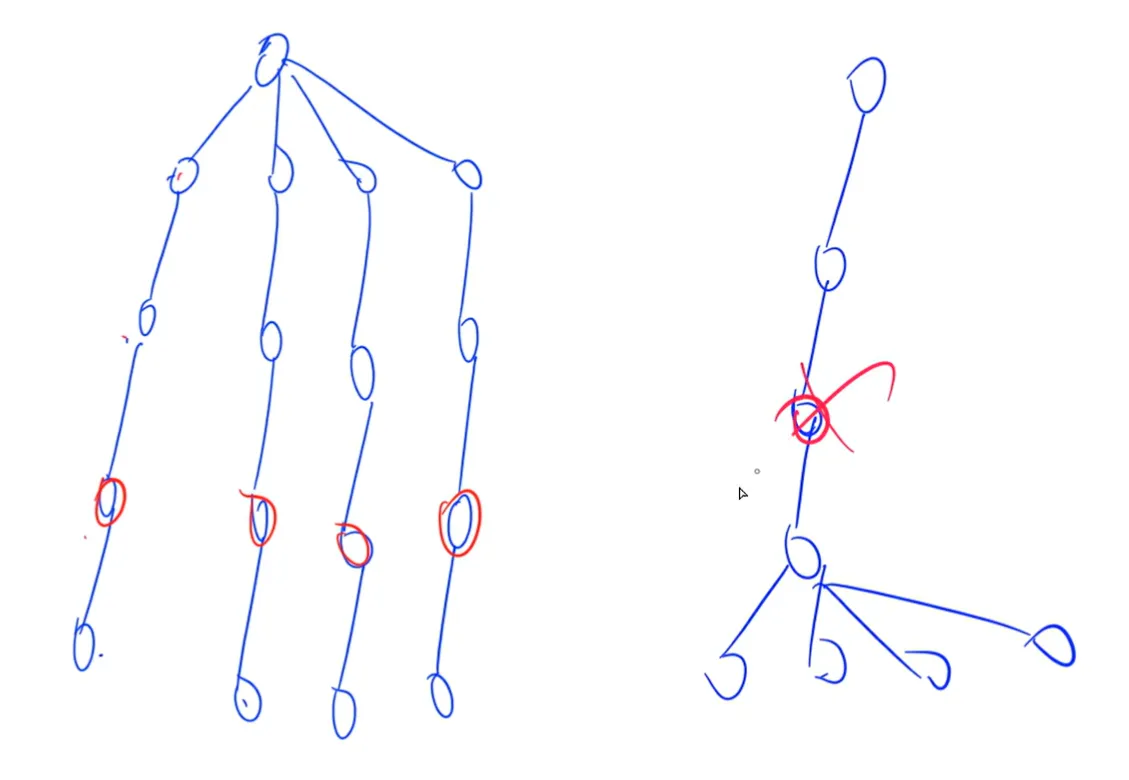
搜索树可能会比较深,但合法方案在一个比较浅的位置。
那么我们可以一层一层地搜,不断增大搜索区,有点像 BFS。
宽搜空间是指数级别的,而迭代加深的复杂度是线性的。
其实就是按照 BFS 方式扩展,按照 DFS 的方式搜索。
AcWing170
比如这道题,最大可以到达 100 层,但是最快 7 层就可以到达,所以没必要搜那么多,就可以用迭代加深来做。
剪枝:
优先枚举较大的数。 排除等效冗余,枚举下一个数的时候,可以枚举之前两个数的和。判断一下每个数有没有被枚举过。 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 110 ;int n;int path[N];bool DFS (int u, int depth) if (u > depth) return false ; bool st[N] = {0 }; if (path[u - 1 ] == n) return true ; for (int i = u - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) for (int j = i; j >=0 ; j--) { int s = path[i] + path[j]; if (s > n || s <= path[u - 1 ] || st[s]) continue ; st[s] = true ; path[u] = s; if (DFS (u + 1 , depth)) return true ; } return false ; } int main () path[0 ] = 1 ; while (cin >> n, n) { int depth = 1 ; while (!DFS (1 , depth)) depth++; for (int i = 0 ; i < depth; ++i) cout << path[i] << ' ' ; cout << endl; } return 0 ; }
与双向 BFS 原理相同。
AcWing171
这个题不能用背包写,因为体积很大。
那就爆搜,以此枚举每个物品选或者不选,那就是 2 46 2^{46} 2 4 6
先看看前一半物品能凑出来的重量有哪些。
那么就是 2 23 2^{23} 2 2 3
然后再枚举后一半的物品选/不选,
那就看下后面有没有 s + l ≤ w s + l \le w s + l ≤ w
那如何找到一个小于等于某个数的最大值呢?二分。
2 N 2 + 2 N 2 × N 2 2^{\frac{N}{2}}+2^{\frac{N}{2}}\times{\frac{N}{2}} 2 2 N + 2 2 N × 2 N
由于第二部分需要用到二分,所以一开始可以多预处理一些,降低总体时间复杂度。
枚举顺序:先枚举大的数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 46 ;typedef long long ll;int n, m;int w[N];int k;int weights[1 << 25 ], cnt = 1 ; int ans;void DFS1 (int u, int s) if (u == k) { weights[cnt++] = s; return ; } DFS1 (u + 1 , s); if ((ll)s + w[u] <= m) DFS1 (u + 1 , s + w[u]); } void DFS2 (int u, int s) if (u == n) { int l = 0 , r = cnt - 1 ; while (l < r) { int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1 ; if (weights[mid] <= m - s) l = mid; else r = mid - 1 ; } ans = max (ans, weights[l] + s); return ; } DFS2 (u + 1 , s); if ((ll)s + w[u] <= m) DFS2 (u + 1 , s + w[u]); } int main () cin >> m >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) cin >> w[i]; sort (w, w + n); reverse (w, w + n); k = n / 2 ; DFS1 (0 , 0 ); sort (weights, weights + cnt); cnt = unique (weights, weights + cnt) - weights; DFS2 (k, 0 ); cout << ans << endl; return 0 ; }
一般配合迭代加深来做
有一个层数上限,在每个节点的位置,都要预估一下最少需要多少步才能得到我想要的答案。
如果一定在层数上限之外的话,那么就要扩大范围,这也相当于迭代加深的一个剪枝。
只需要保证估价函数小于等于真实值 即可,那么正确性就是很显然的。
而且不需要优先队列,所以码量比较小。
AcWing180
对于一段长度为 i i i n − i + 1 n - i + 1 n − i + 1 n − i n - i n − i n − i n - i n − i ( n − i + 1 ) × ( n − i ) (n-i+1)\times(n-i) ( n − i + 1 ) × ( n − i )
于是一共有 ∑ i = 1 n ( n − i + 1 ) × ( n − i ) \sum_{i = 1}^n(n-i+1)\times(n-i) ∑ i = 1 n ( n − i + 1 ) × ( n − i )
这里面是有重复的,比如相对位移是等效的。
所以要除以二。
1 × 2 + 2 × 3 + ⋯ + n × ( n + 1 ) 2 = n × ( n − 1 ) × ( n − 2 ) 3 × 2 \frac{1\times2+2\times3+\dots+n\times(n+1)}{2}=\frac{n\times(n-1)\times(n-2)}{3 \times2} 2 1 × 2 + 2 × 3 + ⋯ + n × ( n + 1 ) = 3 × 2 n × ( n − 1 ) × ( n − 2 )
也就是每次有 560 种选择,一共最多选四次,所以理论复杂度为 56 0 4 560^4 5 6 0 4
最少排多少次?
每次会更改 3 个后继,统计一下序列中所有需要被更改的后继,那么最小更改次数就是 ⌈ t o t 3 ⌉ \lceil\frac{tot}{3}\rceil ⌈ 3 t o t ⌉
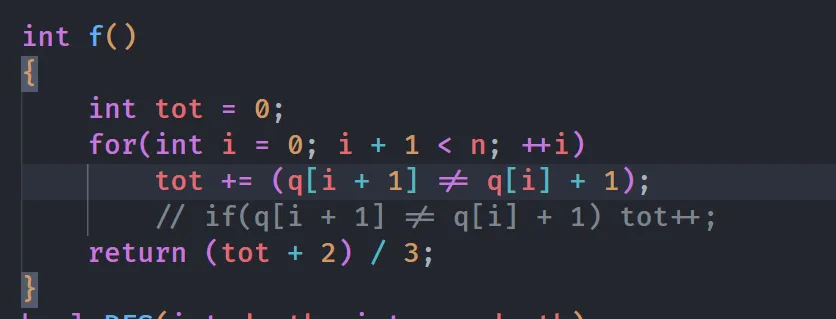
#Q 为什么这样会TLE???
因为判断条件应该先判断深度再去 DFS。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 15 ;int n;int q[N];int w[5 ][N];int f () int tot = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i + 1 < n; ++i) if (q[i + 1 ] != q[i] + 1 ) tot++; return (tot + 2 ) / 3 ; } bool DFS (int depth, int max_depth) if (depth + f () > max_depth) return false ; if (f () == 0 ) return true ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) for (int l = 0 ; l + i - 1 < n; l++) { int r = l + i - 1 ; for (int k = r + 1 ; k < n; k++) { memcpy (w[depth], q, sizeof (q)); int y = l; for (int x = r + 1 ; x <= k; x++, y++) q[y] = w[depth][x]; for (int x = l; x <= r; x++, y++) q[y] = w[depth][x]; if (DFS (depth + 1 , max_depth)) return true ; memcpy (q, w[depth], sizeof (w[depth])); } } return false ; } int main () int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { scanf ("%d" , &n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) scanf ("%d" , &q[i]); int depth = 0 ; while (depth < 5 && !DFS (0 , depth)) depth++; if (depth >= 5 ) puts ("5 or more" ); else printf ("%d\n" , depth); } return 0 ; }
AcWing181
把中间的八个格子变成同一个数,输出最短的一个操作序列(字典序最小);
并且输出最后变成了什么数字。
按照字典序枚举去爆搜就可以得到字典序最小的操作。
可能的操作深度会很深,但是最终答案不会很深,很适合迭代加深。
估价函数:
对于中间八个格子每次把一个格子拉出去,再拉进来,相当于每次只能改变一个格子的值。
然后每次统计一下中间八个格子里出现最多的数,用 8 减去它就是估价,也就是最少需要操作的次数。
对于操作,可以人工打一个表,对每一个操作的序列写出来。
小优化:如果上一次拉了一下,这次不能是反向操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 24 ;int op[8 ][7 ] = { {0 , 2 , 6 , 11 , 15 , 20 , 22 }, {1 , 3 , 8 , 12 , 17 , 21 , 23 }, {10 , 9 , 8 , 7 , 6 , 5 , 4 }, {19 , 18 , 17 , 16 , 15 , 14 , 13 }, {23 , 21 , 17 , 12 , 8 , 3 , 1 }, {22 , 20 , 15 , 11 , 6 , 2 , 0 }, {13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 }, {4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 }, }; int opposite[] = {5 , 4 , 7 , 6 , 1 , 0 , 3 , 2 };int center[] = {6 , 7 , 8 , 11 , 12 , 15 , 16 , 17 };int q[N];int path[100 ];int f () int sum[4 ] = {0 }; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) sum[q[center[i]]]++; int s = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; ++i) s = max (sum[i], s); return 8 - s; } void operate (int x) int t = q[op[x][0 ]]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 6 ; i++) q[op[x][i]] = q[op[x][i + 1 ]]; q[op[x][6 ]] = t; return ; } bool DFS (int depth, int max_depth, int last) if (depth + f () > max_depth) return false ; if (f () == 0 ) return true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i++) if (last != opposite[i]) { operate (i); path[depth] = i; if (DFS (depth + 1 , max_depth, i)) return true ; operate (opposite[i]); } return false ; } int main () while (cin >> q[0 ], q[0 ]) { for (int i = 1 ; i < N; i++) cin >> q[i]; int depth = 0 ; while (!DFS (0 , depth, -1 )) depth++; if (!depth) printf ("No moves needed" ); else { for (int i = 0 ; i < depth; i++) printf ("%c" , path[i] + 'A' ); } printf ("\n%d\n" , q[6 ]); } return 0 ; }
分为最短距离(走迷宫)和最小步数两类问题
最短距离:
在一个二维矩阵中从某个点走到另一个点的最短距离,所有边权相同。
最小步数:
移动地图,使得地图从原来的变成另一种地图所需要的最小步数,每个状态是一个点,状态的转移对应边权为1,也就是求从一个状态转移到另一个状态所需要的最小代价。
顾名思义,洪水填充
每次选择一个新加的格子,看看周围是否有可以扩展的格子。
可以在线性时间内找到某个点所在的连通块。
例题:
AcWing1097
统计连通块的数量。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <queue> #define x first #define y second using namespace std;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 1010 , M = N * N;int n, m, cnt;char g[N][N];bool vis[N][N];void Bfs (int x, int y) queue<PII> q; q.push ({x, y}); vis[x][y] = true ; while (!q.empty ()) { PII t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = t.x - 1 ; i <= t.x + 1 ; ++i) for (int j = t.y - 1 ; j <= t.y + 1 ; ++j) { if (i == t.x && j == t.y) continue ; if (i < 0 || i > n - 1 || j < 0 || j > m - 1 ) continue ; if (g[i][j] == '.' || vis[i][j]) continue ; vis[i][j] = true ; q.push ({i, j}); } } } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) scanf ("%s" , g[i]); int cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) for (int j = 0 ; j < m; ++j) if (g[i][j] == 'W' && !vis[i][j]) { Bfs (i, j); cnt++; } printf ("%d\n" , cnt); return 0 ; }
AcWing1098
统计连通块的数量及大小。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define x first #define y second using namespace std;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 55 , M = N * N;int n, m;int g[N][N];bool vis[N][N];int Bfs (int x, int y) int dx[] = {0 , -1 , 0 , 1 }, dy[] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }; queue<PII> q; int area = 0 ; q.push ({x, y}); vis[x][y] = true ; while (!q.empty ()) { PII t = q.front (); q.pop (); area++; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) { int nx = t.x + dx[i], ny = t.y + dy[i]; if (nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 0 || ny > m) continue ; if (vis[nx][ny]) continue ; if ((g[t.x][t.y] >> i) & 1 ) continue ; q.push ({nx, ny}); vis[nx][ny] = true ; } } return area; } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; ++j) scanf ("%d" , &g[i][j]); int cnt = 0 , area = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; ++j) { if (!vis[i][j]) { area = max (area, Bfs (i, j)); cnt++; } } printf ("%d\n%d\n" , cnt, area); return 0 ; }
AcWing1106
一个连通块周围没有比它低的,它就是山峰;
周围没有比它高的,它就是山谷。
求山峰山谷的数量。
统计每个连通块,统计的时候判断它和周围格子的关系
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define x first #define y second using namespace std;const int N = 1010 ;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int n;int h[N][N];bool vis[N][N];void Bfs (int x, int y, bool &has_higher, bool &has_lower) queue<PII> q; q.push ({x, y}); vis[x][y] = true ; while (!q.empty ()) { PII t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = t.x - 1 ; i <= t.x + 1 ; ++i) for (int j = t.y - 1 ; j <= t.y + 1 ; ++j) { if (i < 1 || i > n || j < 1 || j > n) continue ; if (h[i][j] != h[t.x][t.y]) { if (h[i][j] > h[t.x][t.y]) has_higher = true ; else has_lower = true ; } else if (!vis[i][j]) { q.push ({i, j}); vis[i][j] = true ; } } } } int main () scanf ("%d" , &n); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; ++j) scanf ("%d" , &h[i][j]); int peak = 0 , valley = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; ++j) { if (vis[i][j]) continue ; bool has_higher = false , has_lower = false ; Bfs (i, j, has_higher, has_lower); if (!has_higher) peak++; if (!has_lower) valley++; } printf ("%d %d\n" , peak, valley); return 0 ; }
所有边权都相同,那么就有个性质,由宽搜第一次搜到的就是最短的路。
小证明,给一个边权为 1 的图:
两段性:队列中相邻的两个位置到起点的最短距离最多差一。 单调性:前面都是比较小的一段,后面都是比较大的一段。初始:就一个点,到起点距离为 0 。 假设当前满足,取出一个 x ,然后把它扩展出的没有走过的点都放到队尾,这样一个队列仍然满足性质。 类比一下堆优化的 Dijkstra 算法,当队列不空时,每次选出堆顶,枚举它能到的边,然后更新一遍,出队时一定是最小值。
习题:
AcWing1076
求左上角到右下角的最短路径。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define x first #define y second using namespace std;const int N = 1010 ;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int n;int g[N][N];PII pre[N][N]; PII ans[N * N]; void Bfs (int x, int y) int dx[] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }; int dy[] = {0 , -1 , 0 , 1 }; queue<PII> q; q.push ({x, y}); memset (pre, -1 , sizeof (pre)); pre[x][y] = {n, n}; while (!q.empty ()) { PII t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) { int nx = t.x + dx[i]; int ny = t.y + dy[i]; if (nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 1 || ny > n) continue ; if (g[nx][ny]) continue ; if (pre[nx][ny].x != -1 ) continue ; q.push ({nx, ny}); pre[nx][ny] = t; } } } int main () scanf ("%d" , &n); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; ++j) scanf ("%d" , &g[i][j]); Bfs (n, n); PII end (1 , 1 ) ; while (true ) { printf ("%d %d\n" , end.x - 1 , end.y - 1 ); if (end.x == n && end.y == n) break ; end = pre[end.x][end.y]; } return 0 ; }
AcWing188
走路方式变成了中国象棋的马的步。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define x first #define y second using namespace std;const int N = 155 ;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int n, m;char g[N][N];int dist[N][N];int Bfs () int dx[] = {2 , 2 , -2 , -2 , 1 , -1 , 1 , -1 }; int dy[] = {1 , -1 , 1 , -1 , 2 , 2 , -2 , -2 }; int sx, sy; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) for (int j = 0 ; j < m; ++j) if (g[i][j] == 'K' ) sx = i, sy = j; queue<PII> q; memset (dist, -1 , sizeof (dist)); dist[sx][sy] = 0 ; q.push ({sx, sy}); while (!q.empty ()) { PII t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { int nx = t.x + dx[i]; int ny = t.y + dy[i]; if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue ; if (g[nx][ny] == '*' ) continue ; if (dist[nx][ny] != -1 ) continue ; if (g[nx][ny] == 'H' ) return dist[t.x][t.y] + 1 ; q.push ({nx, ny}); dist[nx][ny] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1 ; } } return -1 ; } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &m, &n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) scanf ("%s" , g[i]); printf ("%d\n" , Bfs ()); return 0 ; }
AcWing1100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 7 ;int n, k;int dist[N];int Bfs () memset (dist, -1 , sizeof (dist)); queue<int > q; q.push (n); dist[n] = 0 ; while (!q.empty ()) { int t = q.front (); q.pop (); if (t == k) return dist[k]; if (t + 1 < N && dist[t + 1 ] == -1 ) { dist[t + 1 ] = dist[t] + 1 ; q.push (t + 1 ); } if (t - 1 >= 0 && dist[t - 1 ] == -1 ) { dist[t - 1 ] = dist[t] + 1 ; q.push (t - 1 ); } if (t * 2 < N && dist[t * 2 ] == -1 ) { dist[t * 2 ] = dist[t] + 1 ; q.push (t * 2 ); } } return -1 ; } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &k); printf ("%d\n" , Bfs ()); }
AcWing173
求每个点到所有 1 的距离的最小值。
分别输出这些最小值。
朴素的做法:分别以每个 1 为起点遍历整张图,保留该点的距离最小值,复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O ( n 2 )
按照最短路的思路,可以建一个虚拟源点,把它像每个 1 连接一条长度为 0 的边,然后跑最短路。
BFS:
一开始把所有 1 的距离初始化为 0 并加到队列里,然后后面就和搜索一样了。
一个点第一次出队时一定是最小值,证明方法同上。
所以每个点只会被更新一次。
A173
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef pair<int , int > PII;#define x first #define y second const int N = 1010 ;int n, m;char g[N][N];int dist[N][N];void BFS () memset (dist, -1 , sizeof (dist)); queue<PII> q; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < m; ++j) { if (g[i][j] == '1' ) { dist[i][j] = 0 ; q.push ({i, j}); } } } int dx[] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }; int dy[] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; while (!q.empty ()) { auto t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) { int nx = t.x + dx[i]; int ny = t.y + dy[i]; if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue ; if (dist[nx][ny] != -1 ) continue ; dist[nx][ny] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1 ; q.push ({nx, ny}); } } } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) scanf ("%s" , g[i]); BFS (); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < m; ++j) printf ("%d " , dist[i][j]); printf ("\n" ); } return 0 ; }
把某个东西从某个状态转移到另外某个状态需要的最少步数。
A1107
给定目标状态,计算最少操作次数以及操作过程,操作过程按照字典序最小输出。
一般字典序不是为了增加难度,而是为了好评,正常写一般就符合条件。
当然可以用康托展开来做。
存状态?哈希
用 unordered_map 来做哈希,它适合查询,而一般的 map 适合存储,详情可以看 unordered_map ;
字典序问题扩展状态的时候按照 ABC 的顺序去扩展即可。
因为这样能保证第一次搜到的永远是字典序最小并且最优的。
code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;char g[2 ][4 ]; unordered_map<string, int > dist; unordered_map<string, pair<char , string> > pre; queue<string> q; void Set (string state) for (int i = 0 ; i <= 3 ; ++i) g[0 ][i] = state[i]; for (int i = 3 , j = 4 ; i >= 0 ; --i, ++j) g[1 ][i] = state[j]; } string Get () string res; for (int i = 0 ; i <= 3 ; ++i) { res += g[0 ][i]; } for (int i = 3 ; i >= 0 ; --i) { res += g[1 ][i]; } return res; } string move0 (string state) Set (state); for (int i = 0 ; i <= 3 ; ++i) swap (g[0 ][i], g[1 ][i]); return Get (); } string move1 (string state) Set (state); char v0 = g[0 ][3 ], v1 = g[1 ][3 ]; for (int i = 3 ; i >= 1 ; --i) { swap (g[0 ][i], g[0 ][i - 1 ]); swap (g[1 ][i], g[1 ][i - 1 ]); } g[0 ][0 ] = v0; g[1 ][0 ] = v1; return Get (); } string move2 (string state) Set (state); char v = g[0 ][1 ]; g[0 ][1 ] = g[1 ][1 ]; g[1 ][1 ] = g[1 ][2 ]; g[1 ][2 ] = g[0 ][2 ]; g[0 ][2 ] = v; return Get (); } void Bfs (string start, string end) if (start == end) return ; q.push (start); dist[start] = 0 ; while (!q.empty ()) { auto t = q.front (); q.pop (); string m[3 ]; m[0 ] = move0 (t); m[1 ] = move1 (t); m[2 ] = move2 (t); for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++i) { string mt = m[i]; if (dist.count (mt) == 0 ) { dist[mt] = dist[t] + 1 ; pre[mt] = {char (i + 'A' ), t}; if (mt == end) break ; q.push (mt); } } } return ; } int main () int x; string start, end; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { scanf ("%d" , &x); end += char (x + '0' ); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) start += char (i + '1' ); Bfs (start, end); printf ("%d\n" , dist[end]); string res; while (end != start) { res += pre[end].first; end = pre[end].second; } reverse (res.begin (), res.end ()); if (res.size ()) cout << res << endl; return 0 ; }
01BFS
A175
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int n,m;char e[550 ][550 ];int dist[550 ][550 ];int dx[]={-1 ,-1 ,1 ,1 };int dy[]={-1 ,1 ,-1 ,1 };inline int read () int x=0 ,y=1 ; char c=getchar (); while (c>'9' ||c<'0' ) { if (c=='-' ) y=-1 ; c=getchar (); } while (c>='0' &&c<='9' ) { x=x*10 +c-'0' ; c=getchar (); } return x*y; } struct point { int x,y,d; point (){} point (int a,int b,int c):x (a),y (b),d (c){} }; void _01BFS(){ deque<point> q; q.push_front (point (0 ,0 ,0 )); dist[0 ][0 ]=0 ; while (!q.empty ()) { point now=q.front (); q.pop_front (); if (now.x==n&&now.y==m) return ; for (int i=0 ;i<4 ;i++) { int nx=now.x+dx[i],ny=now.y+dy[i]; if (nx<0 ||ny<0 ||nx>n||ny>m) continue ; if (i==0 ) { if (e[now.x][now.y]=='\\' ) { if (now.d<dist[nx][ny]) { dist[nx][ny]=now.d; q.push_front (point (nx,ny,dist[nx][ny])); } } else { if (now.d+1 <dist[nx][ny]) { dist[nx][ny]=now.d+1 ; q.push_back (point (nx,ny,dist[nx][ny])); } } } if (i==1 ) { if (e[now.x][now.y+1 ]=='/' ) { if (now.d<dist[nx][ny]) { dist[nx][ny]=now.d; q.push_front (point (nx,ny,dist[nx][ny])); } } else { if (now.d+1 <dist[nx][ny]) { dist[nx][ny]=now.d+1 ; q.push_back (point (nx,ny,dist[nx][ny])); } } } if (i==2 ) { if (e[now.x+1 ][now.y]=='/' ) { if (now.d<dist[nx][ny]) { dist[nx][ny]=now.d; q.push_front (point (nx,ny,dist[nx][ny])); } } else { if (now.d+1 <dist[nx][ny]) { dist[nx][ny]=now.d+1 ; q.push_back (point (nx,ny,dist[nx][ny])); } } } if (i==3 ) { if (e[now.x+1 ][now.y+1 ]=='\\' ) { if (now.d<dist[nx][ny]) { dist[nx][ny]=now.d; q.push_front (point (nx,ny,dist[nx][ny])); } } else { if (now.d+1 <dist[nx][ny]) { dist[nx][ny]=now.d+1 ; q.push_back (point (nx,ny,dist[nx][ny])); } } } } } } int main () int T; scanf ("%d" , &T); while (T--) { n=read (),m=read (); for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) scanf ("%s" ,e[i]+1 ); if ((n+m)%2 !=0 ) { cout<<"NO SOLUTION" <<endl; continue ; } for (int i=0 ;i<=n;i++) for (int j=0 ;j<=m;j++) dist[i][j]=0x7fffffff ; _01BFS(); printf ("%d\n" ,dist[n][m]); } return 0 ; }
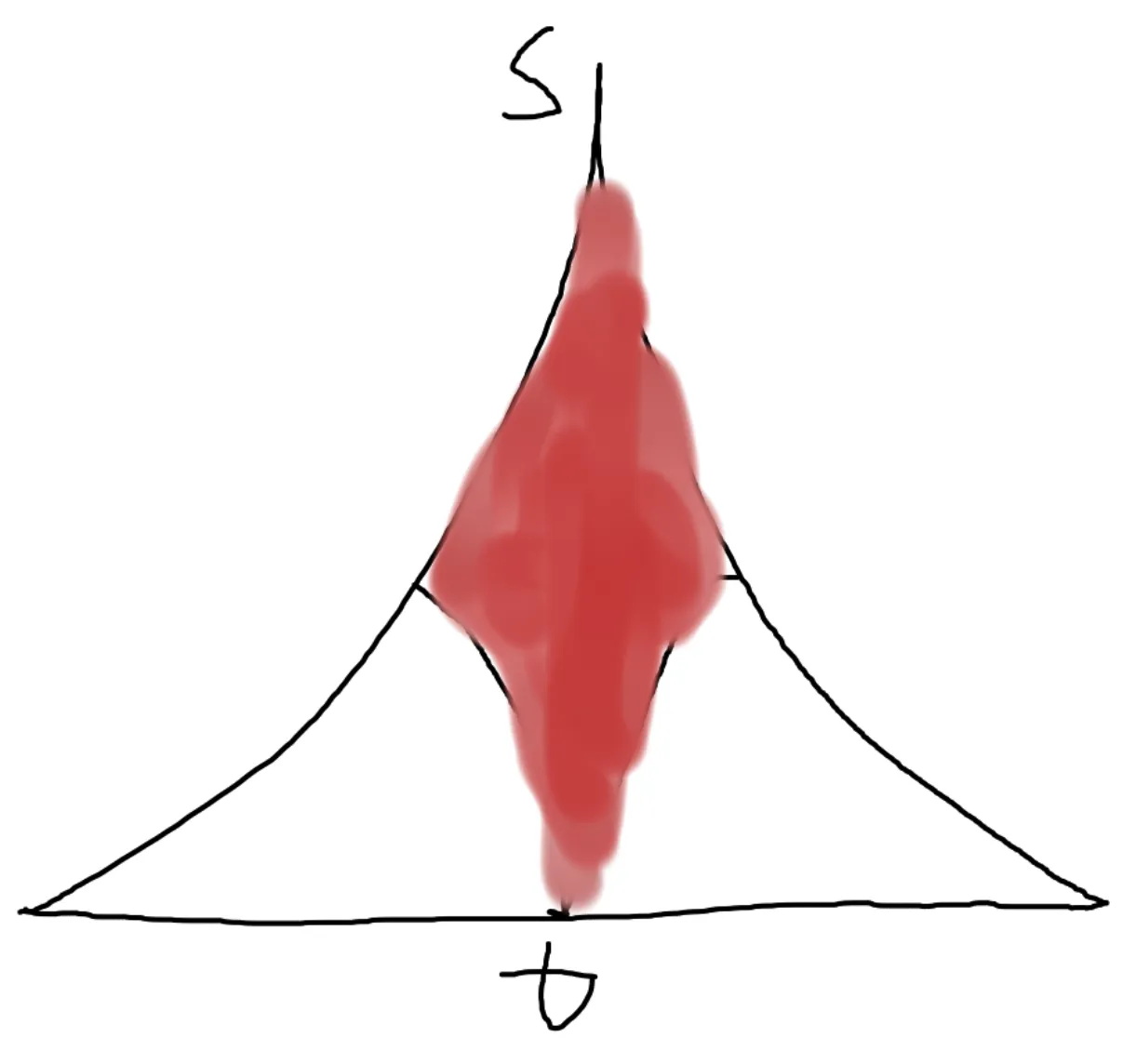
状态较少的时候,其实就和普通 BFS 差不多,比如 最短路模型 或者 洪水填充 。
但是状态变多的时候,就可能会超时,比如 最小步数模型 。
在 BFS 中,每一层新加的点都是上一层的两倍,也就是说这是一个指数增加的过程。
比如这样,就只需要搜红色面积内的点,大大节约了时间和空间。
小优化:每次选择元素较少的方向扩展。
字串变换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 6 ;int n;string a[N], b[N]; int extend (queue<string> &q, unordered_map<string, int > &da, unordered_map<string, int > &db, string a[], string b[]) string t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < (int )t.size (); ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; ++j) { if (t.substr (i, a[j].size ()) == a[j]) { string state = t.substr (0 , i) + b[j] + t.substr (i + a[j].size ()); if (db.count (state)) return da[t] + 1 + db[state]; if (da.count (state)) continue ; da[state] = da[t] + 1 ; q.push (state); } } } return 11 ; } int Bfs (string A, string B) if (A == B) return 0 ; queue<string> qa, qb; unordered_map<string, int > da, db; qa.push (A), da[A] = 0 ; qb.push (B), db[B] = 0 ; while (qa.size () && qb.size ()) { int t; if (qa.size () <= qb.size ()) t = extend (qa, da, db, a, b); else t = extend (qb, db, da, b, a); if (t <= 10 ) return t; } return 11 ; } int main () string A, B; cin >> A >> B; while (cin >> a[n] >> b[n]) ++n; int step = Bfs (A, B); if (step > 10 ) printf ("NO ANSWER!" ); else printf ("%d\n" , step); return 0 ; }
一种结合了 Dijkstra 和贪心最优原则的一种搜索算法。
应用场景:和双向广搜一样,都是求最短距离,但是状态空间非常庞大 (步数小的时候直接 BFS 即可),直接搜会搜到非常多的状态,导致超时。
所以需要加上一个启发函数,作用是从起点开始搜,搜非常少的状态就可以求出起点到终点的最短路径。
把 BFS 中的队列换为优先队列(小根堆) 每个状态(预测距离)存真实距离(起点走到当前点)加上估计距离(当前点到终点),也就是存到当前这条路径到终点的估计值,每次挑一个预测距离最小的点来扩展。 终点第一次出队时,循环结束。 满足估计距离小于等于真实距离 ,这样才可以满足出队的时候 距离才是最小的。 满足有解,不然还会全搜一遍,还不如 BFS。 估价函数返回值 ∈ [ 0 , d ] \in{[0,d]} ∈ [ 0 , d ] d d d 反证法:假设终点第一次出队的时候不是最小值,即d i s t ( t ) > d dist(t)>d d i s t ( t ) > d u u u
d ( u ) + f ( u ) < = d ( u ) + g ( u ) = d d(u) + f(u) <= d(u) + g(u) = d d ( u ) + f ( u ) < = d ( u ) + g ( u ) = d
∴ d ( t ) + f ( t ) = d i s t ( t ) > d ≥ d ( u ) + f ( u ) \therefore d(t) + f(t) = dist(t) > d \ge d(u) + f(u) ∴ d ( t ) + f ( t ) = d i s t ( t ) > d ≥ d ( u ) + f ( u )
也就是假如队列里有最优解,那么它的估计距离一定是最小的,所以最优解一定最先出队,否则与优先队列规则,优先出 f + d f + d f + d
所以出队的时候一定是最小值。
它只能保证终点出队的时候距离最小,但不能保证其他点出队的时候是最小值(算法竞赛-进阶指南的错误)。
比如对于这样一个例子,这个交点它就不成立,并且每个点不一定只被扩展一次(除了终点)。
然后接着放下走把终点入队的时候,发现队列里有比这个情况小的预测距离,所以就会“拨乱反正”,重新走正确的路径,那么接着出队的时候,这条新路肯定已经被走完了,此时终点距离已经被更新成了最小值。
BFS:每个状态只会入队一次,所以入队的时候进行判重。 Dijkstra:每个状态只会出队一次,所以可以出队的时候判重。 SPFA:每个状态在每个时刻最多在队列中出现一次,所以可以在入队的时候判重。 A-star:每个状态不一定只入队一次或出队一次,所以不能判重。 估计距离一般用经典的估价函数,否则满足要求即可。
把八个数字放到一个九宫格里,每次可以移动一个数字到空闲位置,现给定一个初始状态,求最小步数得到终止状态:
任意输出一种最小步数的方案即可。
有解的充要条件:序列的逆序对数量为偶数,如果为奇数,那么就一定无解。
有解的话,逆序对数量一定是偶数。如果是行内移动,那么逆序对数量不会变。
而往上/下移动,相当于把它移动到某两个数的前面/后面,也就是说只改变了两对逆序对。
也就是说每次移动不会改变逆序对数量的奇偶性,而末状态的逆序对数量为偶数(0),所以逆序对数量必须是奇数。
那么偶数一定是有解的,奇数一定是无解的。
估价函数:
每次移动只会改变某个数的一个位置,于是估价函数可以取当前状态的每一个数字和目标位置的曼哈顿距离之和。
因为不能直接过去,需要迂回一下,所以是满足估计距离小于等于实际距离 这样一个条件的。
Acwing179
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef pair<int , string> PIS;#define x first #define y second string ed ("12345678x" ) ;int f (string state) int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < (int )state.size (); ++i) if (state[i] != 'x' ) { int t = state[i] - '1' ; res += abs (i / 3 - t / 3 ) + abs (i % 3 - t % 3 ); } return res; } string Bfs (string start) unordered_map<string, int > dist; unordered_map<string, pair<char , string> > prev; priority_queue<PIS, vector<PIS>, greater<PIS> > heap; dist[start] = 0 ; heap.push ({f (start), start}); char op[] = "urdl" ; int dx[] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }, dy[] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; while (heap.size ()) { auto t = heap.top (); heap.pop (); string state = t.y; if (state == ed) break ; int nx, ny; for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; ++i) { if (state[i] == 'x' ) { nx = i / 3 ; ny = i % 3 ; break ; } } string source = state; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) { int a = nx + dx[i], b = ny + dy[i]; if (a < 0 || a > 2 || b < 0 || b > 2 ) continue ; state = source; swap (state[nx * 3 + ny], state[a * 3 + b]); if (!dist.count (state) || dist[state] > dist[source] + 1 ) { dist[state] = dist[source] + 1 ; prev[state] = {op[i], source}; heap.push ({dist[state] + f (state), state}); } } } string res; while (ed != start) { res += prev[ed].x; ed = prev[ed].y; } reverse (res.begin (), res.end ()); return res; } int main () string start, seq; char c; while (cin >> c) { start += c; if (c != 'x' ) seq += c; } int cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) for (int j = i; j < 8 ; ++j) if (seq[i] > seq[j]) cnt++; if (cnt & 1 ) printf ("unsolvable" ); else cout << Bfs (start) << endl; return 0 ; }
P1379
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define x first #define y second typedef pair<int , string> PIS;string ed ("123804765" ) ;int lox[] = {0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 2 , 2 , 2 , 1 };int loy[] = {0 , 1 , 2 , 2 , 2 , 1 , 0 , 0 };int f (string state) int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < (int )state.size (); ++i) { if (state[i] != '0' ) { int t = state[i] - '0' ; res += abs (i / 3 - lox[t]) + abs (i % 3 - loy[t]); } } return res; } int Bfs (string start) unordered_map<string, int > dist; unordered_map<string, pair<char , string> > prev; priority_queue<PIS, vector<PIS>, greater<PIS> > heap; dist[start] = 0 ; heap.push ({f (start), start}); int dx[] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }, dy[] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; while (heap.size ()) { auto t = heap.top (); heap.pop (); string state = t.y; if (state == ed) break ; int nx, ny; for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; ++i) { if (state[i] == '0' ) { nx = i / 3 ; ny = i % 3 ; break ; } } string source = state; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) { int a = nx + dx[i], b = ny + dy[i]; if (a < 0 || a > 2 || b < 0 || b > 2 ) continue ; state = source; swap (state[nx * 3 + ny], state[a * 3 + b]); if (!dist.count (state) || dist[state] > dist[source] + 1 ) { dist[state] = dist[source] + 1 ; heap.push ({dist[state] + f (state), state}); } } } return dist[ed]; } int main () string start; cin >> start; cout << Bfs (start) << endl; return 0 ; }
爆搜,且搜索范围很大,很适合 A-star
估价:
以当前点到终点的最短距离作为估价函数,因为它一定小于等于实际走的距离。
既然第一次弹出是距离最小的,那么第 k k k k k k
先看第二次:
与第一次证明思路相同,
运用数学归纳法,可得第 k k k k k k
注意,是弹出时的该状态,而不是 d i s t dist d i s t d i s t dist d i s t
AcWing178
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 1000 , M = 200010 ;#define x first #define y second typedef pair<int , int > PII;typedef pair<int , PII> PIII;struct edge { int nxt, val, to; }e[M]; int fir[N], rfir[N];int n, m, S, T, K;int cnt, tot;bool vis[N];int dist[N];void Add (int u, int v, int w, bool direc) e[++cnt].to = v; e[cnt].val = w; if (direc) { e[cnt].nxt = fir[u]; fir[u] = cnt; } else { e[cnt].nxt = rfir[u]; rfir[u] = cnt; } } void Dijkstra (int s) priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII> > heap; memset (dist, 0x3f , sizeof (dist)); dist[s] = 0 ; heap.push ({0 , s}); while (heap.size ()) { auto t = heap.top (); heap.pop (); int ver = t.y; if (vis[ver]) continue ; vis[ver] = true ; for (int i = rfir[ver]; i; i = e[i].nxt) { int v = e[i].to; if (dist[v] > dist[ver] + e[i].val) { dist[v] = dist[ver] + e[i].val; heap.push ({dist[v], v}); } } } } int Astar () priority_queue<PIII, vector<PIII>, greater<PIII> > heap; heap.push ({dist[S], {0 , S}}); while (heap.size ()) { auto t = heap.top (); heap.pop (); int ver = t.y.y; int d = t.y.x; if (ver == T) tot++; if (tot == K) return d; for (int i = fir[ver]; i; i = e[i].nxt) { int v = e[i].to; if (dist[v] == 0x3f3f3f3f ) continue ; heap.push ({d + e[i].val + dist[v], {d + e[i].val, v}}); } } return -1 ; } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; ++i) { int a, b, c; scanf ("%d%d%d" , &a, &b, &c); Add (a, b, c, true ); Add (b, a, c, false ); } scanf ("%d%d%d" , &S, &T, &K); if (S == T) K++; Dijkstra (T); printf ("%d\n" , Astar ()); return 0 ; }
在一个多峰函数上行走,每次可以走一小步,当且仅当向左和向右走都不是更优的时候,我就停下,否则就向更优的方向走。
但是这样有一个问题,我们找到的“最优解”很可能是“局部最优解”。
因为这本身就是一个贪心的思路。
所以需要加一些东西使这个贪心找到正确答案的概率更高一些。
基于爬山算法,加上了温度T 参数作为控制步子大小的参数。
温度越高,就容易冲动从而一步走得很大,这样就会波动到全局最优解,但是很不稳定。
温度渐渐降下来时,冷静下来后每次的步子就走的比较小了,这样最后就会在全局最优解附近不断逼近直至找到最优解。
虽然说也有可能在局部最优解就冷静下来了,不过没关系,你多重复几次这样的过程,得到正解的概率就会大大增加。
先设置一个初始温度,每次操作后进行一个降温操作,即T T T
还要设一个满足条件的初始答案,在此基础上进行调整(这个答案不必很准确,尽量接近答案以减少迭代次数)。
每次走一步后,如果是更优解,那么就走过去;如果不是更优解,那就以一定的概率走过去,这个是平衡概率e x p ( Δ E / T ) exp(\Delta{E}/T) e x p ( Δ E / T ) e x p exp e x p e e e
如果怕参数没调校好导致超时,或者是想尽量多重复几次步骤,可以尝试加入卡时 技巧。
如:
1 if ((double )clock ()/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<T) break ;
其中 T 为时限,记得预留足够的输出时间。
会有0 ∼ 5 m s 0\sim{5} ms 0 ∼ 5 m s
一种区间暴力结合分块的玄学优化的离线算法。莫涛大神的知乎
如果题目要求强制在线的话,线段树和树状数组才是更优选择。
给定一个序列,每次询问为一个区间,每次输出该区间内共有多少不同的数。
对于这道题,暴力的做法肯定是把每个区间都扫一遍,扫的时候统计区间内不同书的个数。
而这个的一个优化就是移动区间的左右端点的指针。
初始时l = 1 , r = 0 l=1,r=0 l = 1 , r = 0 c n t cnt c n t
而每遇到一个新数,就把它出现的次数加一,如果它出现的次数是零,那么说明这个数在之前都没有出现过,所以不同数的个数也要加一。假如这个数字之前出现过了,那么就只加对应数的个数,而不需要加不同数的个数。
每减去一个数,把它的出现次数减一,这时候判断一下是否为零,如果是,那就说明这个数已经消失了,所以不同数的个数也要减一。
具体的实现过程,注意++和--的顺序:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 void add (int pos) if (!cnt[a[pos]]) ++now; ++cnt[a[pos]]; } void del (int pos) --cnt[a[pos]]; if (!cnt[a[pos]]) --now; } void work () for (int i=1 ;i<=q;i++) { int ql,qr; scanf ("%d%d" ,&qr,&ql); while (l<ql) del (l++); while (l>ql) add (--l); while (r<qr) add (++r); while (r>qr) del (r--); printf ("%d" ,now); } }
但这还不够,因为在一些极端情况下,比如中间有一段很长的区间,但是查询都是在两端的小区间,而且还是换着来的,这样就会导致区间一会跑向左边,一会跑向右边,就会被卡。
所以我们就要上一些玄学优化 了。
将长度为n n n n \sqrt{n} n 1 1 1 n \sqrt{n} n
排序函数:
1 2 3 4 bool cmp (query a, query b) return belong[a.l]==belong[b.l]?a.r<b.r:belong[a.l]<belong[b.l]; }
这么一个优化就把时间复杂度从n 2 n^2 n 2 n n n\sqrt{n} n n
对于左端点在同一个编号为奇数的块内,右端点按照升序排列。
对于左端点在统一编号为偶数的块内,右端点按照降序排列。
它的主要原理便是右指针跳完奇数块往回跳时在同一个方向能顺路把偶数块跳完,然后跳完这个偶数块又能顺带把下一个奇数块跳完。
1 2 3 4 int cmp (query a, query b) return (belong[a.l]^belong[b.l])?belong[a.l]<belong[b.l]:((belong[a.l]&1 )?a.r<b.r:a.r>b.r); }
先用异或判断两个数是否相等,如果不同,那么就按照编号升序排序;如果相同,那么再比较它们的块的编号的奇偶性,如果是奇数,那就按照右端点升序排序,否则按照右端点降序排序。
1 2 3 4 while (l<ql) now-=!--cnt[a[l++]];while (l>ql) now+=!cnt[a[--l]]++;while (r<qr) now+=!cnt[a[++r]]++;while (r>qr) now-=!--cnt[a[r--]];
注意此处+=优先级比cnt++更高
略。
参考文章: